BEETS+ Ingredients
All your healthy heart essentials

Organic Beet Root
A superfood rich in nitrates which helps support healthy blood pressure, heart health, circulation and energy levels†
Healthy Blood Pressure†
Nitric Oxide Production†
Supports Blood Flow†

Prebiotics
Inulin derived from chicory root, a soluble dietary fiber that supports gut health and digestive function†
Gut Health & Digestion†

Vitamins B6, B12, C
Vitamins key in maintaining energy levels and supporting the immune system†
Heart Health†
Liver Health & Detox†

Clean Energy†

Thiamin
Also known as Vitamin B1, and essential vitamin that plays a vital role in overall health†

Clean Energy†

Turmeric Root Powder
(95% curcumin)
A polyphenol with anti-inflammatory properties to support gut function and metabolic health†
Gut Health & Digestion†

Superfruits
Pomegranate, bilberry fruit, and maqui berry - superfruits celebrated for their potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties†
Heart Health†

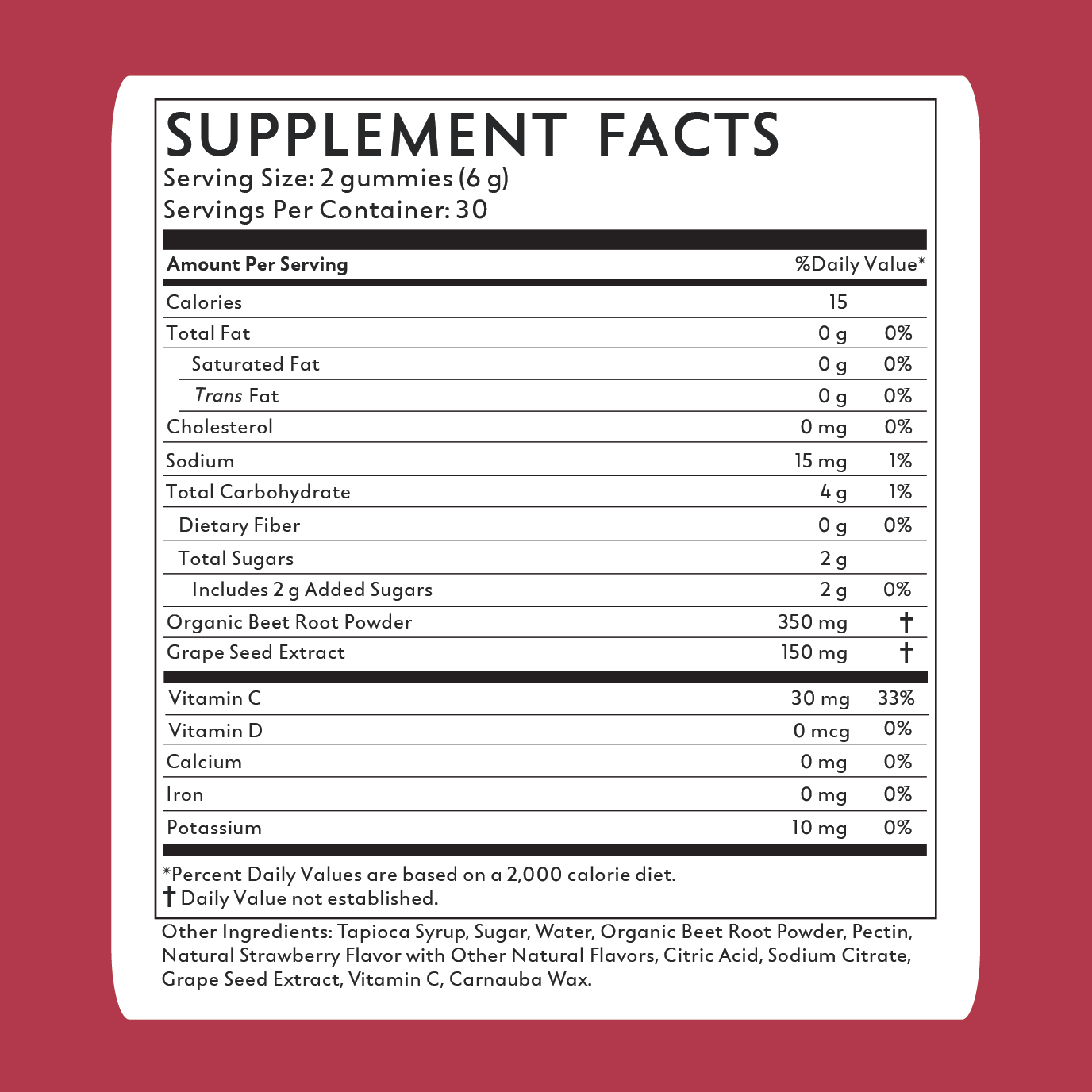
BEETS+ Gummies Ingredients
All your healthy heart essentials

Organic Beet Root
A superfood rich in nitrates which helps support healthy blood pressure, heart health, circulation and energy levels†
Healthy Blood Pressure†
Nitric Oxide Production†
Supports Blood Flow†

Grape Seed Extract
Derived from the seeds of grapes, this versatile supplement supports healthy blood pressure and heart health (among other things)†
Supports Blood Flow†

Improves Cognitive Health†
Nitric Oxide Production†

Vitamin C
A vital nutrient that supports immune function and overall health†
Heart Health†
Liver Health & Detox†

Clean Energy†

Organic Beet Root
A superfood rich in nitrates which helps support healthy blood pressure, heart health, circulation and energy levels†
Healthy Blood Pressure†
Nitric Oxide Production†
Supports Blood Flow†

Grape Seed Extract
Derived from the seeds of grapes, this versatile supplement supports healthy blood pressure and heart health (among other things)†
Supports Blood Flow†

Improves Cognitive Health†
Nitric Oxide Production†

Vitamin C
A vital nutrient that supports immune function and overall health†
Heart Health†
Liver Health & Detox†

Clean Energy†